Radon gas builds up in homes and has serious health effects. Reducing radon gas in homes is cheap and easy with a slab floor barrier with proper sealing at junctions and evacuation stack which can vent naturally, or have a mechanical radon gas extractor fan fitted, depending on the levels of Radon in your home.
Radon (Rn) is a natural gas resulting from the decay of uranium, present everywhere in the earth's crust. Outside, the gas is released into the atmosphere where its concentration is of no concern.

Modern construction techniques have us building homes far more airtight than in previous decades for reasons of durability (condensation in wall assemblies), and also for energy efficiency, as air leakage used to account for about 1/3 the total heat loss of a home. The lack of fresh air leaking in and out when building green homes means radon now collects in homes at higher concentrations and it has become a greater health concern.
Radon is colorless and odorless and can be present in any home without humans being able to realize or detect it. Radon gas exists everywhere, but some regions have much higher concentrations than others.
A study by Health Canada over two years showed that 6.9% of Canadians live in homes where radon concentration exceeds this line radon guideline of 200 Bq / m3. Health Canada advises homeowners to evaluate radon levels of their properties and investigate ways to mitigate it. Radon mostly enters through the basements, and the natural stack effect of homes means air from the basement will find its way to the top floors. More specifically, radon penetrates through:
- Stone foundations
- Crawl spaces
- Floor drains
- Un-sealed sump pump housings
- Cracks, gaps and joints in walls, floors, ceilings
- Openings around pipes
- Well Water
What are the health effects of radon gas?
Exposure to high levels of radon gas in air is the second greatest cause of lung cancer after smoking, estimated to account for about 16% of all cases of lung cancer.
According to Health Canada, "the only known health risk associated with exposure to radon in indoor air is an increased risk of developing lung cancer." It depends on the average concentration of the gas in the building, of the duration of exposure and smoking. The exposure does not cause other known disorders such special breathing problems or headaches. If ingested, radon is harmless.
Protecting air quality from reduced radon levels is easily done as new homes are being constructed, it becomes a bit more tricky retrofitting older homes.
Radon testing should be carried out in all homes
While many people rely on radon gas maps by State in the US and province in Canada to decide whether to test their homes for radon, official advice is actually to test first then ask questions later. We have seen homes built side by side, and built the same way, which tested dramatically differently for radon gas in their basements. Carbon Monoxide in homes may have the reputation as the "silent killer", but we say it's better to be safe than sorry and test your home for radon gas as a matter of course, but especially if you've ever heard of any reports of there being radon gas in the area.

Is there radon gas in water?
Yes, unfortunately radon is water-soluble and can enter homes that rely on well water, particularly as water is aerated by showers and sinks. Links to cancer due to breathing air contaminated with high levels of radon are well estatblished, but there are also indications that consuming radon-rich water has health hazards as well. Learn how to remove radon gas from well water here - before it gets in the home, or indeed you!
"While the science is still in it’s early stages and the results aren’t yet conclusive, studies indicate that there are links between ingesting water contaminated with high levels of radon gas and stomach cancer, colon cancer and some types of blood cancer.” - David Innes, Radon Environmental
Radon evacuation stacks:
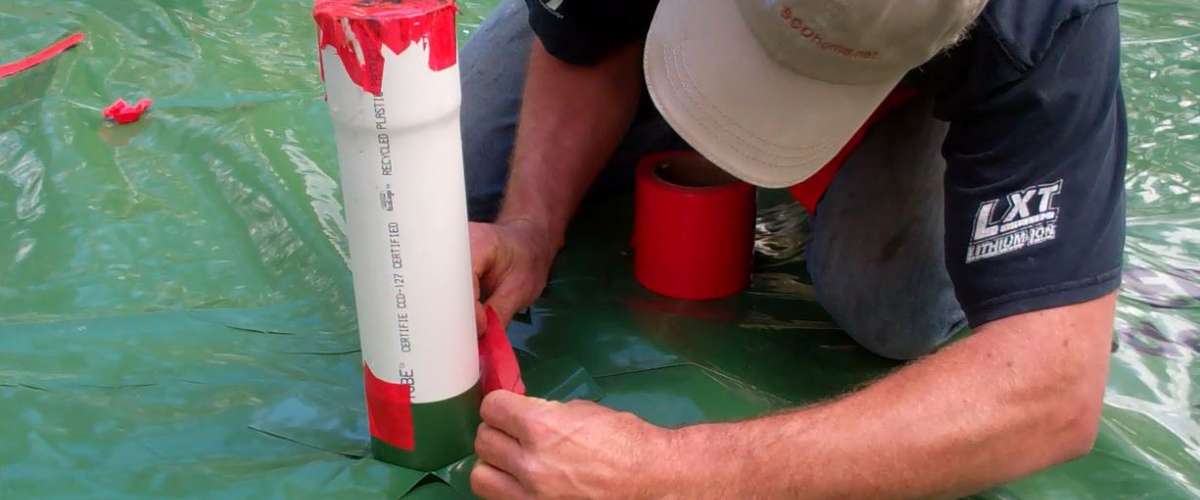
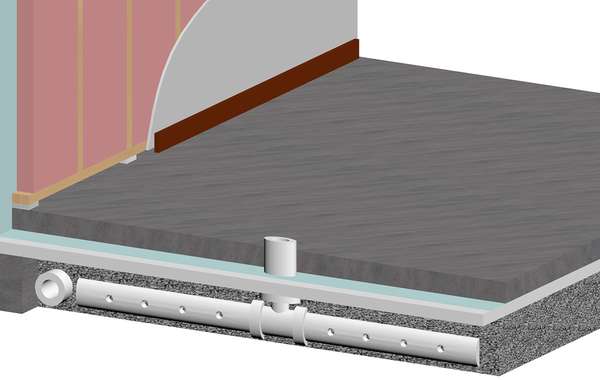
A radon stack can be passive or active. A properly installed sub-slab barrier and passive stack is a great start, and in higher risk areas or with trickier situations of retrofitting existing homes, a fan can be installed in the stack that increases the draw. There are numerous techniques for lowering radon levels no matter the situation.
Green home passive radon evacuation stacks:
Before concrete slabs are poured, the addition of a well sealed vapour/radon barrier and a simple PVC tube and a T-junction can give radon gas an easy escape route. It is a very simple and low-cost procedure that has great results in reducing radon levels in homes simply due to the natural stack effect. An electrical junction box should be located near the stack in order to allow for the installation of a fan if testing of the home reveals that it is necessary.
Radon mitigation in basements & crawlspaces:
Removing radon from basements and crawlspaces is easier if prevented rather than cured, and existing homes that are found to have high levels of radon should look at mitigation asap. Depending on the state of your basement and or crawlspace, there will be varying degrees of difficulty in mitigating radon.
Crawlspaces can often be fitted with a radon stack and membrane barrier, finished basements and those with already poured concrete floors will probably prove a bit more difficult. As the awareness of the danger of radon gas becomes more common, you are not left to deal with this on your own as contractors are regularly popping up that specialize in reducing home radon levels.
Now you know more about the dangers of radon gas in homes and how to test for radon. Find more pages about radon mitigation in basements and crawl spaces and how to maintain healthy indoor air quality here:
Find more about green home construction in the Ecohome Green Building Guide pages - Also, learn more about the benefits of a free Ecohome Network Membership here. |


































Hi, question. If I want to build an ultra tiny house of 10 feet by 10, the pipe system won't work because it'll be too close to the windows. Do I have any options for active mitigation?